阿里员工都在看的Java 集合详解,不能错过!
发布于 2021-05-08 12:00 ,所属分类:JAVA工程师开发学习资料

1.集合框架
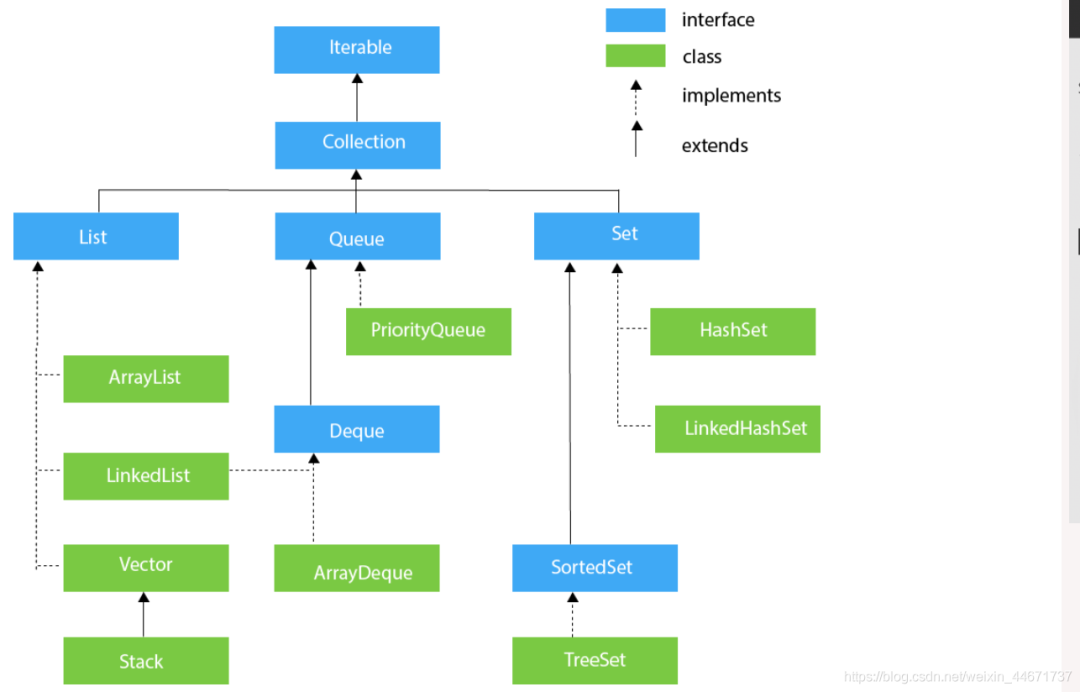
1.1 顶层接口Iterable
//支持lambda函数接口
importjava.util.function.Consumer;
publicinterfaceIterable<T>{
//iterator()方法
Iterator<T>iterator();
defaultvoidforEach(Consumer<?superT> action){
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for(T t :this) {
action.accept(t);
}
}
defaultSpliterator<T>spliterator(){
returnSpliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(),0);
}
}
packagejava.util;
importjava.util.function.Predicate;
importjava.util.stream.Stream;
importjava.util.stream.StreamSupport;
publicinterfaceCollection<E>extendsIterable<E>{
intsize();
booleanisEmpty();
booleancontains(Object o);
Iterator<E>iterator();
Object[] toArray();
booleanadd(E e);
booleanremove(Object o);
booleancontainsAll(Collection<?> c);
booleanremoveAll(Collection<?> c);
defaultbooleanremoveIf(Predicate<?superE> filter){
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
booleanremoved =false;
finalIterator<E> each = iterator();
while(each.hasNext()) {
if(filter.test(each.next())) {
each.remove();
removed =true;
}
}
returnremoved;
}
booleanretainAll(Collection<?> c);
voidclear();
inthashCode();
@Override
defaultSpliterator<E>spliterator(){
returnSpliterators.spliterator(this,0);
}
defaultStream<E>stream(){
returnStreamSupport.stream(spliterator(),false);
}
defaultStream<E>parallelStream(){
returnStreamSupport.stream(spliterator(),true);
}
}
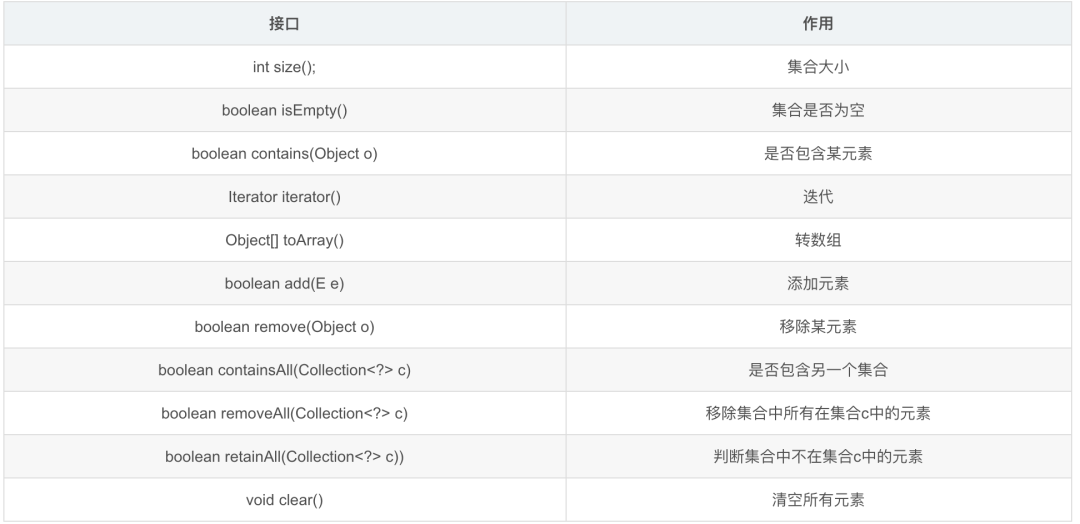
2.1 List接口
packagejava.util;
importjava.util.function.UnaryOperator;
publicinterfaceList<E>extendsCollection<E>{
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
booleanaddAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
booleanaddAll(intindex, Collection<? extends E> c);
defaultvoidreplaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator){
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
finalListIterator<E> li =this.listIterator();
while(li.hasNext()) {
li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
}
}
defaultvoidsort(Comparator<?superE> c){
Object[] a =this.toArray();
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator<E> i =this.listIterator();
for(Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
}
booleanequals(Object o);
Eget(intindex);
Eset(intindex, E element);
voidadd(intindex, E element);
intindexOf(Object o);
intlastIndexOf(Object o);
ListIterator<E>listIterator();
List<E>subList(intfromIndex,inttoIndex);
@Override
defaultSpliterator<E>spliterator(){
returnSpliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
}
2.2 List实现ArrayList
ArrayList是List接口最常用的一个实现类,支持List接口的一些列操作。
2.2.1 ArrayList继承关系
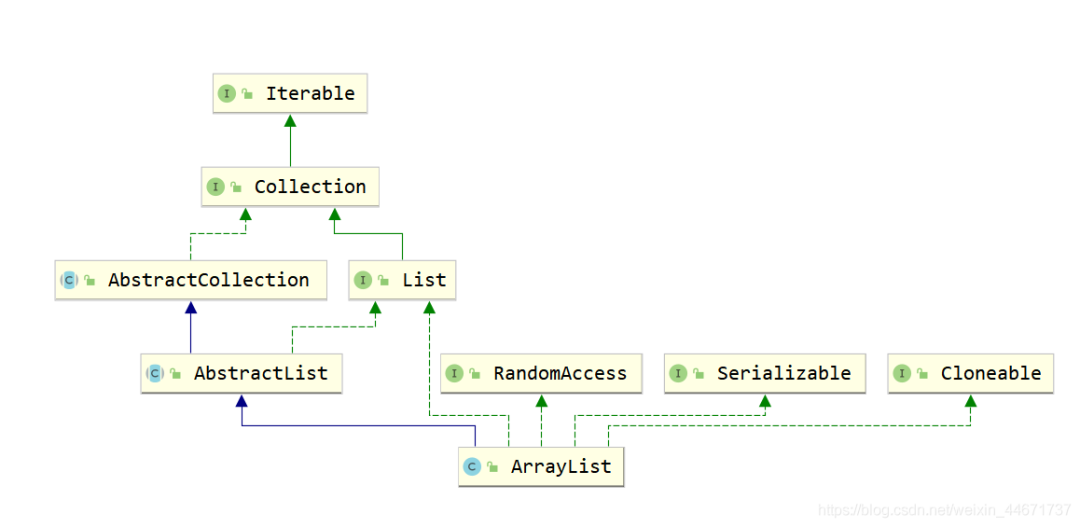
2.2.2 ArrayList组成
privatestaticfinalObject[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
privatestaticfinalObject[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}
//真正存放元素的数组
transientObject[] elementData;// non-private to simplify nested class access
privateintsize;
2.2.3 ArrayList构造函数
publicArrayList(intinitialCapacity){
if(initialCapacity >0) {
this.elementData =newObject[initialCapacity];
}elseif(initialCapacity ==0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}else{
thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
publicArrayList(){
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
2.2.4 ArrayList中添加元素
publicbooleanadd(E e){
ensureCapacityInternal(size +1);// Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
returntrue;
}
2.2.4 ArrayList扩容
privatestaticintcalculateCapacity(Object[] elementData,intminCapacity){
if(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//DEFAULT_CAPACITY是10
returnMath.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
returnminCapacity;
}
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity>>1);
privatevoidgrow(intminCapacity){
// overflow-conscious code
intoldCapacity = elementData.length;
intnewCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >>1);
if(newCapacity - minCapacity <0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if(newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE >0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2.2.5 数组copy
publicstaticnativevoidarraycopy(Object src,intsrcPos,
Object dest,intdestPos,
intlength);
p = (int*)malloc(len*sizeof(int));
2.2.6 why?elementData用transient修饰?
1. transient的作用是该属性不参与序列化。
2. ArrayList继承了标示序列化的Serializable接口
privatevoidwriteObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throwsjava.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
intexpectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for(inti=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if(modCount != expectedModCount) {
thrownewConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is,
* deserialize it).
*/
privatevoidreadObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throwsjava.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt();// ignored
if(size >0) {
// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
intcapacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size);
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);
ensureCapacityInternal(size);
Object[] a = elementData;
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for(inti=0; i<size; i++) {
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}
}
protectedtransientintmodCount =0;
2.3 LinkedList
2.3.1 LinkedList继承关系
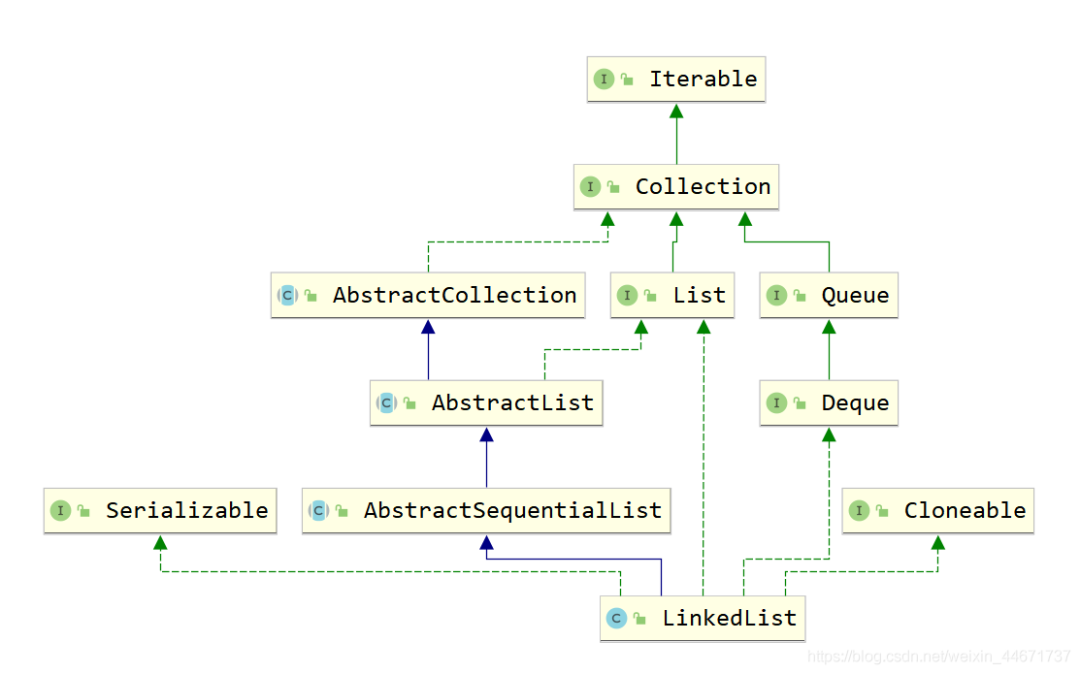
2.3.2 LinkedList的结构
transientNode<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transientNode<E> last;
privatestaticclassNode<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
transientintsize =0;
transientNode<E> first;
transientNode<E> last;
publicLinkedList(){
}
/**
* Links e as first element. 头插法
*/
privatevoidlinkFirst(E e){
finalNode<E> f = first;
finalNode<E> newNode =newNode<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if(f ==null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Links e as last element. 尾插法
*/
voidlinkLast(E e){
finalNode<E> l = last;
finalNode<E> newNode =newNode<>(l, e,null);
last = newNode;
if(l ==null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
2.3.3 LinkedList查询方法
publicEget(intindex){
checkElementIndex(index);
returnnode(index).item;
}
Node<E>node(intindex){
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//判断index更靠近头部还是尾部
if(index < (size >>1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for(inti =0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
returnx;
}else{
Node<E> x = last;
for(inti = size -1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
returnx;
}
}
publicEset(intindex, E element){
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
returnoldVal;
}
2.4.3 LinkedList修改方法
publicbooleanadd(E e){
linkLast(e);
returntrue;
}
2.5 Vector
2.5.1 vector组成
//存放元素的数组
protectedObject[] elementData;
//有效元素数量,小于等于数组长度
protectedintelementCount;
//容量增加量,和扩容相关
protectedintcapacityIncrement;
2.5.2 vector线程安全性
2.5.3 vector扩容
privatevoidgrow(intminCapacity){
// overflow-conscious code
intoldCapacity = elementData.length;
//扩容大小
intnewCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement >0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if(newCapacity - minCapacity <0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if(newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE >0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2.5.4 vector方法经典示例
publicsynchronizedEremove(intindex){
modCount++;
if(index >= elementCount)
thrownewArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
intnumMoved = elementCount - index -1;
if(numMoved >0)
//复制数组,假设数组移除了中间某元素,后边有效值前移1位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//引用null ,gc会处理
elementData[--elementCount] =null;// Let gc do its work
returnoldValue;
}
2.6 Stack
2.6.1 Stack的继承关系

2.6.2 Stack的使用
Stack<String> strings =newStack<>();
strings.push("aaa");
strings.push("bbb");
strings.push("ccc");
System.err.println(strings.pop());

2.6.3 Stack源码
/**
* Stack源码(Jdk8)
*/
public
classStack<E>extendsVector<E>{
publicStack(){
}
//入栈,使用的是Vector的addElement方法。
publicEpush(E item){
addElement(item);
returnitem;
}
//出栈,找到数组最后一个元素,移除并返回。
publicsynchronizedEpop(){
E obj;
intlen = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len -1);
returnobj;
}
publicsynchronizedEpeek(){
intlen = size();
if(len ==0)
thrownewEmptyStackException();
returnelementAt(len -1);
}
publicbooleanempty(){
returnsize() ==0;
}
publicsynchronizedintsearch(Object o){
inti = lastIndexOf(o);
if(i >=0) {
returnsize() - i;
}
return-1;
}
privatestaticfinallongserialVersionUID =1224463164541339165L;
}
3.Queue
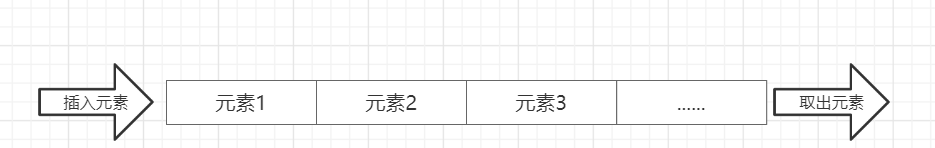
3.1 什么是Deque

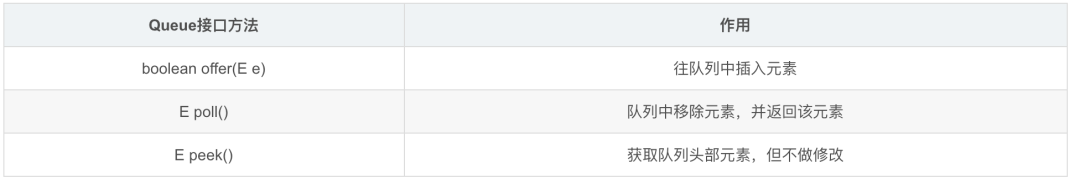
3.1.1 Java中的Queue接口
packagejava.util;
publicinterfaceQueue<E>extendsCollection<E>{
//集合中插入元素
booleanadd(E e);
//队列中插入元素
booleanoffer(E e);
//移除元素,当集合为空,抛出异常
Eremove();
//移除队列头部元素并返回,如果为空,返回null
Epoll();
//查询集合第一个元素,如果为空,抛出异常
Eelement();
//查询队列中第一个元素,如果为空,返回null
Epeek();
}
3.1.2 Deque接口
packagejava.util;
publicinterfaceDeque<E>extendsQueue<E>{
//deque的操作方法
voidaddFirst(E e);
voidaddLast(E e);
booleanofferFirst(E e);
booleanofferLast(E e);
EremoveFirst();
EremoveLast();
EpollFirst();
EpollLast();
EgetFirst();
EgetLast();
EpeekFirst();
EpeekLast();
booleanremoveFirstOccurrence(Object o);
booleanremoveLastOccurrence(Object o);
// *** Queue methods ***
booleanadd(E e);
booleanoffer(E e);
Eremove();
Epoll();
Eelement();
Epeek();
// 省略一堆stack接口方法和collection接口方法
}
3.1.3 Queue,Deque的实现类
3.2 PriorityQueue
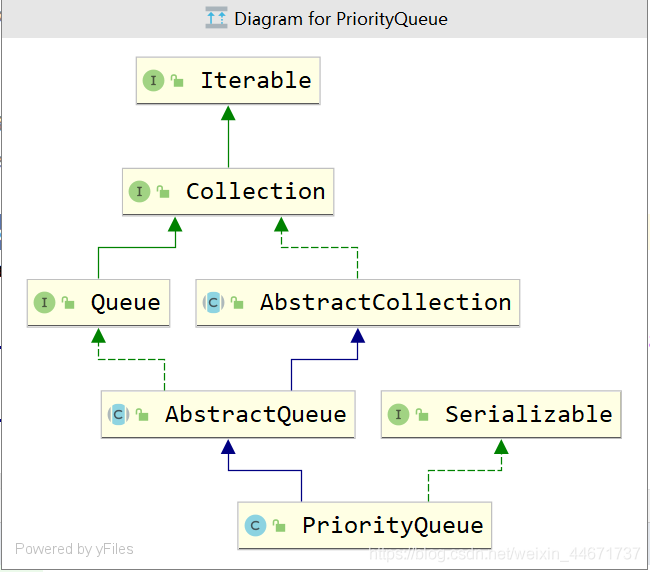
3.2.1 PriorityQueue继承关系
3.2.2 PriorityQueue的使用
PriorityQueue<Integer>queue=newPriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(20);queue.add(14);queue.add(21);queue.add(8);queue.add(9);
queue.add(11);queue.add(13);queue.add(10);queue.add(12);queue.add(15);
while(queue.size()>0){
Integer poll =queue.poll();
System.err.print(poll+"->");
}

// 必须实现Comparable方法,想String,数值本身即可比较
privatestaticclassTestimplementsComparable<Test>{
privateinta;
publicTest(inta){
this.a = a;
}
publicintgetA(){
returna;
}
publicvoidsetA(inta){
this.a = a;
}
@Override
publicStringtoString(){
return"Test{"+
"a="+ a +
'}';
}
@Override
publicintcompareTo(Test o){
return0;
}
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
PriorityQueue<Test>queue=newPriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(newTest(20));queue.add(newTest(14));queue.add(newTest(21));queue.add(newTest(8));queue.add(newTest(9));
queue.add(newTest(11));queue.add(newTest(13));queue.add(newTest(10));queue.add(newTest(12));queue.add(newTest(15));
while(queue.size()>0){
Test poll =queue.poll();
System.err.print(poll+"->");
}
}

3.2.3 PriorityQueue组成
/**
* 默认容量大小,数组大小
*/
privatestaticfinalintDEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY =11;
/**
* 存放元素的数组
*/
transient Object[]queue;// non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* 队列中存放了多少元素
*/
privateintsize =0;
/**
* 自定义的比较规则,有该规则时优先使用,否则使用元素实现的Comparable接口方法。
*/
privatefinal Comparator<? super E> comparator;
/**
* 队列修改次数,每次存取都算一次修改
*/
transientintmodCount =0;// non-private to simplify nested class access
3.2.4 PriorityQueue操作方法
offer方法
publicbooleanoffer(E e){
if(e == null)
thrownewNullPointerException();
modCount++;
inti = size;
if(i >=queue.length)
grow(i +1);
size = i +1;
//i=size,当queue为空的时候
if(i ==0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
returntrue;
}
privatevoidsiftUp(intk, E x){
if(comparator !=null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
privatevoidsiftUpComparable(intk, E x){
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while(k >0) {
//为什么-1, 思考数组位置0,1,2。0是1和2的父节点
intparent = (k -1) >>>1;
//父节点
Object e =queue[parent];
//当传入的新节点大于父节点则不做处理,否则二者交换
if(key.compareTo((E) e) >=0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
pool方法
publicEpoll(){
if(size ==0)
returnnull;
ints = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E)queue[0];
//s = --size,即原来数组的最后一个元素
E x = (E)queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if(s !=0)
siftDown(0, x);
returnresult;
}
privatevoidsiftDownComparable(intk, E x){
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
inthalf = size >>>1;// loop while a non-leaf
while(k < half) {
intchild = (k <<1) +1;// assume left child is least
Object c =queue[child];
intright = child +1;
if(right < size &&
//c和right是parent的两个子节点,找出小的那个成为新的c。
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E)queue[right]) >0)
c =queue[child = right];
if(key.compareTo((E) c) <=0)
break;
//小的变成了新的父节点
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
3.3 ArrayDeque
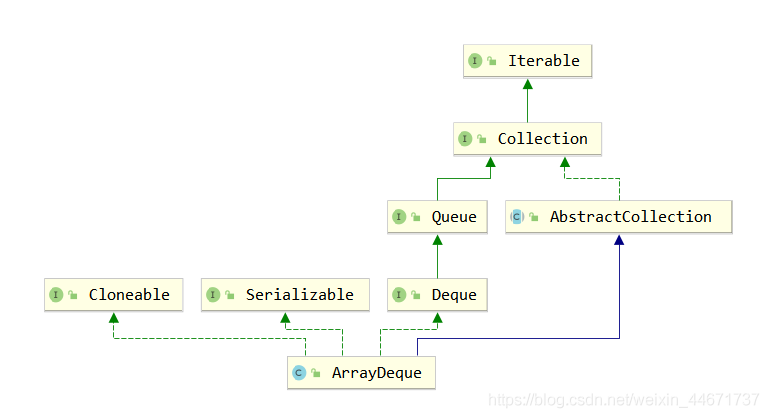
3.3.1 ArrayDeque的继承关系
3.3.2 ArrayDeque使用
ArrayDeque<String>deque=newArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer("aaa");
deque.offer("bbb");
deque.offer("ccc");
deque.offer("ddd");
//peek方法只获取不移除
System.err.println(deque.peekFirst());
System.err.println(deque.peekLast());

ArrayDeque<String>deque=newArrayDeque<>();
deque.offerFirst("aaa");
deque.offerLast("bbb");
deque.offerFirst("ccc");
deque.offerLast("ddd");
String a;
while((a =deque.pollLast())!=null){
System.err.print(a+"->");
}

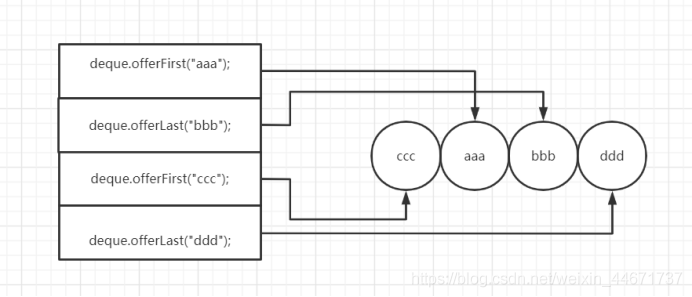
3.3.4 ArrayDeque内部组成
//具体存放元素的数组,数组大小一定是2的幂次方
transientObject[] elements;// non-private to
//队列头索引
transientinthead;
//队列尾索引
transientinttail;
//默认的最小初始化容量,即传入的容量小于8容量为8,而默认容量是16
privatestaticfinalintMIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY =8;
3.3.5 数组elements长度
privatestaticintcalculateSize(intnumElements){
intinitialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// Find the best power of two to hold elements.
// Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
if(numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>>1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>>2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>>4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>>8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>>16);
initialCapacity++;
if(initialCapacity <0)// Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>=1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
returninitialCapacity;
}
3.3.6 ArrayDeque实现机制
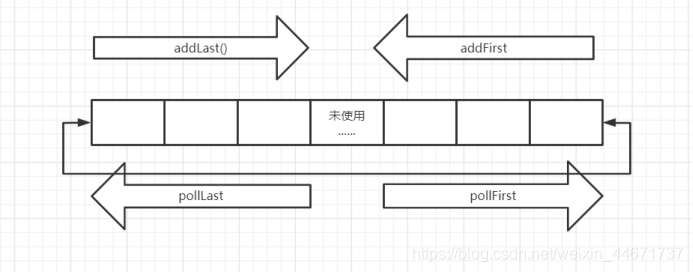
源码:
publicvoidaddFirst(E e){
if(e ==null)
thrownewNullPointerException();
elements[head = (head -1) & (elements.length -1)] = e;
if(head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
head= (head -1) & (elements.length -1)
head= head-1>=0?head-1:elements.length-1
publicvoidaddLast(E e){
if(e ==null)
thrownewNullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
if( (tail = (tail +1) & (elements.length -1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
(tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1))
tail = tail+1>element-1?0:tail+1,是不是很神奇的写法,其原理是一个二进制数全部由1组成和一个大于它的数做&运算结果为0,如10000&1111 = 0。poll方法和add方法逻辑是相反的,此处就不再赘述,诸君共求之!4.1 Set接口
packagejava.util;
publicinterfaceSet<E>extendsCollection<E>{
// Query Operations
intsize();
booleanisEmpty();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
booleanadd(E e);
booleanremove(Object o);
booleancontainsAll(Collection<?> c);
booleanaddAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
booleanretainAll(Collection<?> c);
booleanremoveAll(Collection<?> c);
voidclear();
booleanequals(Object o);
inthashCode();
//此处和Collection接口由区别
Spliterator<E>spliterator(){
returnSpliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
}
4.2 HashSet
4.2.1 HashSet继承关系
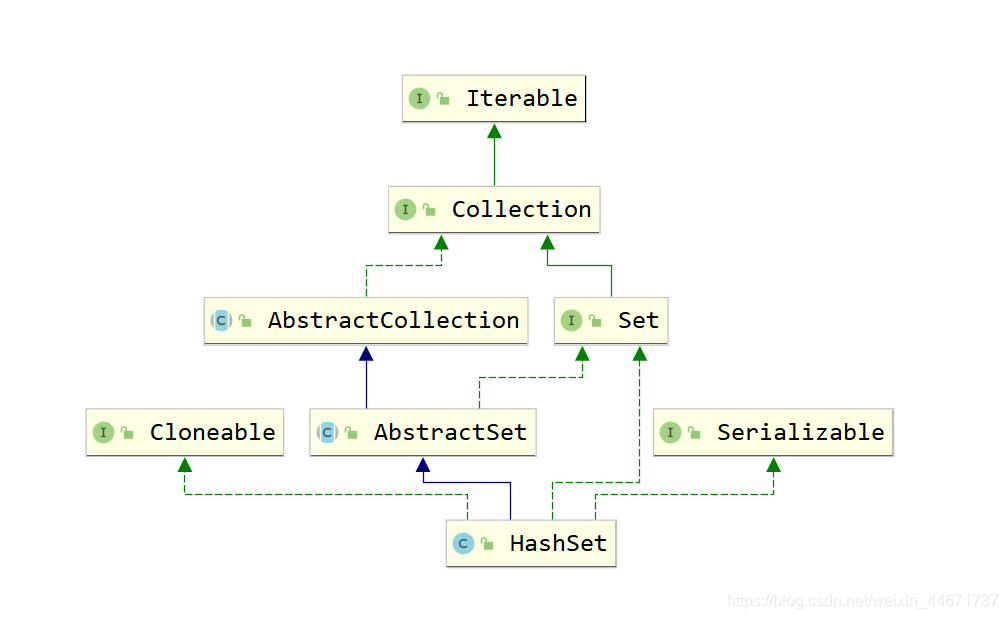
4.2.3 HashSet源码
publicclassHashSet<E>
extendsAbstractSet<E>
implementsSet<E>,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable
{
staticfinallongserialVersionUID =-5024744406713321676L;
privatetransient HashMap<E,Object>map;
privatestaticfinal Object PRESENT =newObject();
publicHashSet(){
map=newHashMap<>();
}
publicHashSet(Collection<? extends E> c){
map=newHashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) +1,16));
addAll(c);
}
publicHashSet(intinitialCapacity,floatloadFactor){
map=newHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
publicHashSet(intinitialCapacity){
map=newHashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
HashSet(intinitialCapacity,floatloadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map=newLinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
publicIterator<E> iterator() {
returnmap.keySet().iterator();
}
publicintsize(){
returnmap.size();
}
publicbooleanisEmpty(){
returnmap.isEmpty();
}
publicbooleancontains(Object o){
returnmap.containsKey(o);
}
publicbooleanadd(E e){
returnmap.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
publicbooleanremove(Object o){
returnmap.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
publicvoidclear(){
map.clear();
}
}
4.2.4 HashSet是如何保证不重复的呢?
4.3 LinkedHashSet
4.3.1 LinkedHashSet继承关系

4.3.2 LinkedHashSet源码
packagejava.util;
publicclassLinkedHashSet<E>
extendsHashSet<E>
implementsSet<E>,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable{
privatestaticfinallongserialVersionUID = -2851667679971038690L;
publicLinkedHashSet(intinitialCapacity,floatloadFactor){
//调用HashSet的构造方法
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor,true);
}
publicLinkedHashSet(intinitialCapacity){
super(initialCapacity, .75f,true);
}
publicLinkedHashSet(){
super(16, .75f,true);
}
publicLinkedHashSet(Collection<? extends E> c){
super(Math.max(2*c.size(),11), .75f,true);
addAll(c);
}
@Override
publicSpliterator<E>spliterator(){
returnSpliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.DISTINCT |
Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
}
2.LinkedHashSet中用于存储值的实现LinkedHashMap,而HashSet使用的是HashMap。LinkedHashSet中调用的父类构造器,可以看到其实列是一个LinkedHashMap。
HashSet(intinitialCapacity,floatloadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map=newLinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
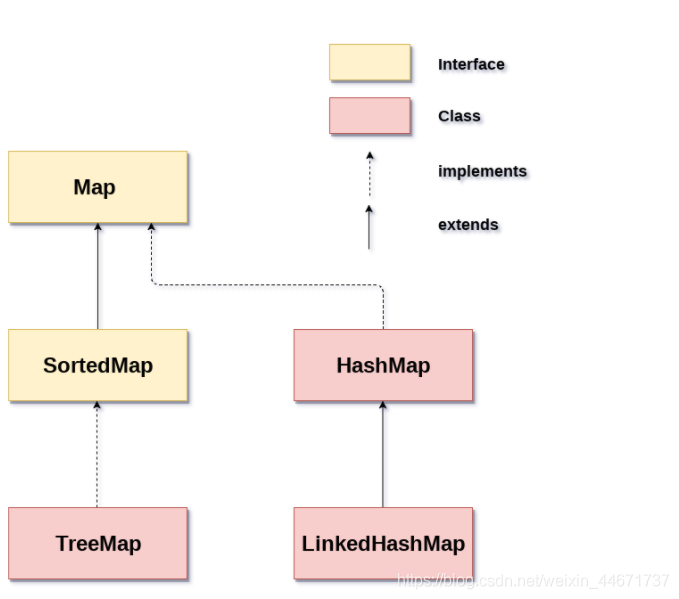
5.1 Map接口
package java.util;
importjava.util.function.BiConsumer;
importjava.util.function.BiFunction;
importjava.util.function.Function;
importjava.io.Serializable;
publicinterfaceMap<K,V> {
// Query Operations
int size();
booleanisEmpty();
booleancontainsKey(Objectkey);
booleancontainsValue(Objectvalue);
Vget(Objectkey);
// Modification Operations
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Objectkey);
// Bulk Operations
voidputAll(Map<?extendsK, ?extendsV> m);
voidclear();
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
interfaceEntry<K,V> {
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
booleanequals(Objecto);
int hashCode();
publicstatic<KextendsComparable<?superK>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {
return(Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
}
publicstatic<K, VextendsComparable<?superV>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {
return(Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());
}
publicstatic<K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<?superK> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return(Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());
}
publicstatic<K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<?superV> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return(Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());
}
}
// Comparison and hashing
booleanequals(Objecto);
int hashCode();
defaultV getOrDefault(Objectkey, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return(((v =get(key)) !=null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
}
defaultvoidforEach(BiConsumer<?superK, ?superV> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for(Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try{
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
}catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
thrownewConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
}
defaultvoidreplaceAll(BiFunction<?superK, ?superV, ?extendsV>function){
Objects.requireNonNull(function);
for(Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try{
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
}catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
thrownewConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
// ise thrown from function is not a cme.
v =function.apply(k, v);
try{
entry.setValue(v);
}catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
thrownewConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
}
}
defaultV putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
V v =get(key);
if(v ==null) {
v = put(key, value);
}
returnv;
}
defaultbooleanremove(Objectkey,Objectvalue) {
ObjectcurValue =get(key);
if(!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||
(curValue ==null&& !containsKey(key))) {
returnfalse;
}
remove(key);
returntrue;
}
defaultbooleanreplace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
ObjectcurValue =get(key);
if(!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||
(curValue ==null&& !containsKey(key))) {
returnfalse;
}
put(key, newValue);
returntrue;
}
defaultV replace(K key, V value) {
V curValue;
if(((curValue =get(key)) !=null) || containsKey(key)) {
curValue = put(key, value);
}
returncurValue;
}
defaultV computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<?superK, ?extendsV> mappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);
V v;
if((v =get(key)) ==null) {
V newValue;
if((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) !=null) {
put(key, newValue);
returnnewValue;
}
}
returnv;
}
defaultV computeIfPresent(K key,
BiFunction<?superK, ?superV, ?extendsV> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue;
if((oldValue =get(key)) !=null) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if(newValue !=null) {
put(key, newValue);
returnnewValue;
}else{
remove(key);
returnnull;
}
}else{
returnnull;
}
}
defaultV compute(K key,
BiFunction<?superK, ?superV, ?extendsV> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue =get(key);
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if(newValue ==null) {
// delete mapping
if(oldValue !=null|| containsKey(key)) {
// something to remove
remove(key);
returnnull;
}else{
// nothing to do. Leave things as they were.
returnnull;
}
}else{
// add or replace old mapping
put(key, newValue);
returnnewValue;
}
}
defaultV merge(K key, V value,
BiFunction<?superV, ?superV, ?extendsV> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
Objects.requireNonNull(value);
V oldValue =get(key);
V newValue = (oldValue ==null) ? value :
remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);
if(newValue ==null) {
remove(key);
}else{
put(key, newValue);
}
returnnewValue;
}
}
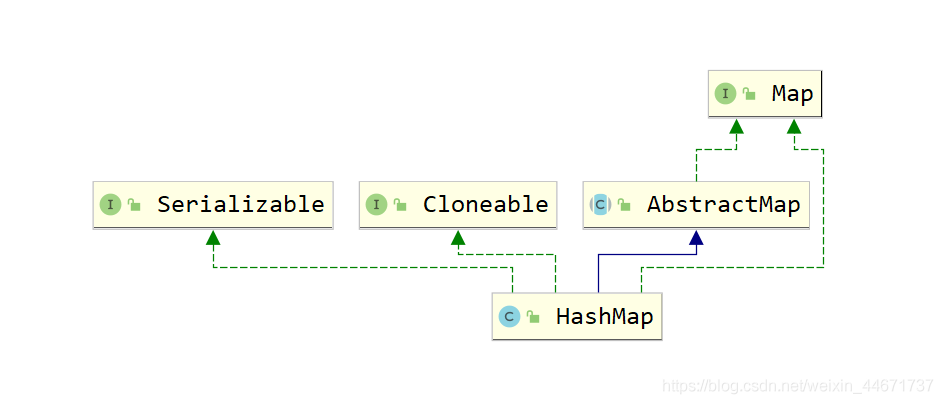
5.2 HashMap
5.2.1 HashMap继承关系
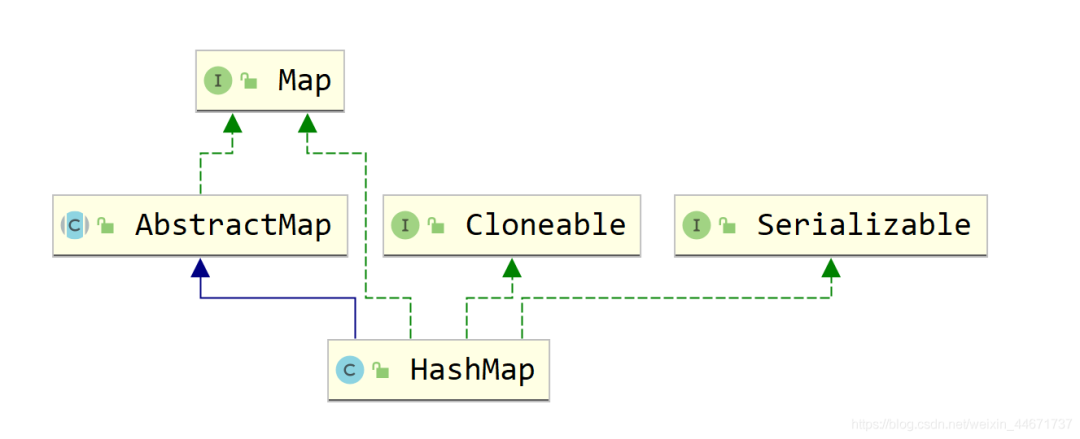
5.2.2 HashMap存储的数据
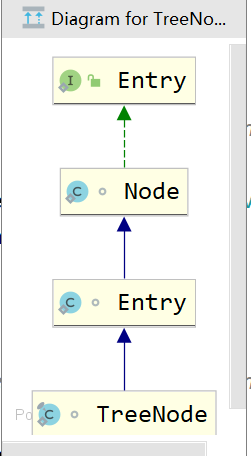
transient Node<K,V>[]table;

5.2.3 HashMap的组成
//是hashMap的最小容量16,容量就是数组的大小也就是变量,transient Node<K,V>[] table。
staticfinalintDEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY =1<<4;// aka 16
//最大数量,该数组最大值为2^31一次方。
staticfinalintMAXIMUM_CAPACITY =1<<30;
//默认的加载因子,如果构造的时候不传则为0.75
staticfinalfloatDEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR =0.75f;
//一个位置里存放的节点转化成树的阈值,也就是8,比如数组里有一个node,这个
// node链表的长度达到该值才会转化为红黑树。
staticfinalintTREEIFY_THRESHOLD =8;
//当一个反树化的阈值,当这个node长度减少到该值就会从树转化成链表
staticfinalintUNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD =6;
//满足节点变成树的另一个条件,就是存放node的数组长度要达到64
staticfinalintMIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY =64;
//具体存放数据的数组
transientNode<K,V>[] table;
//entrySet,一个存放k-v缓冲区
transientSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
//size是指hashMap中存放了多少个键值对
transientintsize;
//对map的修改次数
transientintmodCount;
//加载因子
finalfloatloadFactor;
5.2.4 HashMap中的构造函数
//只有容量,initialCapacity
publicHashMap(intinitialCapacity){
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
publicHashMap(){
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;// all other fields defaulted
}
publicHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m){
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m,false);
}
finalvoidputMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict){
ints = m.size();
if(s >0) {
if(table ==null) {// pre-size
floatft = ((float)s / loadFactor) +1.0F;
intt = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if(t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
elseif(s > threshold)
resize();
for(Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
Vvalue= e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key,value,false, evict);
}
}
}
publicHashMap(intinitialCapacity,floatloadFactor){
if(initialCapacity <0)// 容量不能为负数
thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
//当容量大于2^31就取最大值1<<31;
if(initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if(loadFactor <=0|| Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: "+
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//当前数组table的大小,一定是是2的幂次方
// tableSizeFor保证了数组一定是是2的幂次方,是大于initialCapacity最结进的值。
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
staticfinal int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
intn = cap -1;
n|= n >>>1;
n|= n >>>2;
n|= n >>>4;
n|= n >>>8;
n|= n >>>16;
return(n <0) ?1: (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n +1;
}
5.2.5 put方法
publicVput(K key, Vvalue){
returnputVal(hash(key), key,value,false,true);
}
final VputVal(inthash, K key, Vvalue, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict){
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p;intn, i;
if((tab = table) ==null|| (n = tab.length) ==0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//当hash到的位置,该位置为null的时候,存放一个新node放入
// 这儿p赋值成了table该位置的node值
if((p = tab[i = (n -1) & hash]) ==null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key,value,null);
else{
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//该位置第一个就是查找到的值,将p赋给e
if(p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key !=null&& key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//如果是红黑树,调用红黑树的putTreeVal方法
elseif(p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key,value);
else{
//是链表,遍历,注意e = p.next这个一直将下一节点赋值给e,直到尾部,注意开头是++binCount
for(intbinCount =0; ; ++binCount) {
if((e = p.next) ==null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key,value,null);
//当链表长度大于等于7,插入第8位,树化
if(binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD -1)// -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if(e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key !=null&& key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if(e !=null) {// existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if(!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue ==null)
e.value=value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
returnoldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if(++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
returnnull;
}
5.2.6 查找方法
final Node<K,V>getNode(inthash, Object key){
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e;intn; K k;
//先判断表不为空
if((tab = table) !=null&& (n = tab.length) >0&&
//这一行是找到要查询的Key在table中的位置,table是存放HashMap中每一个Node的数组。
(first = tab[(n -1) & hash]) !=null) {
//Node可能是一个链表或者树,先判断根节点是否是要查询的key,就是根节点,方便后续遍历Node写法并且
//对于只有根节点的Node直接判断
if(first.hash == hash &&// always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key !=null&& key.equals(k))))
returnfirst;
//有子节点
if((e = first.next) !=null) {
//红黑树查找
if(first instanceof TreeNode)
return((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do{
//链表查找
if(e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key !=null&& key.equals(k))))
returne;
}
//遍历链表,当链表后续为null则推出循环
while((e = e.next) !=null);
}
}
returnnull;
}
5.3 HashTable
5.3.1 HashTable的类继承关系图
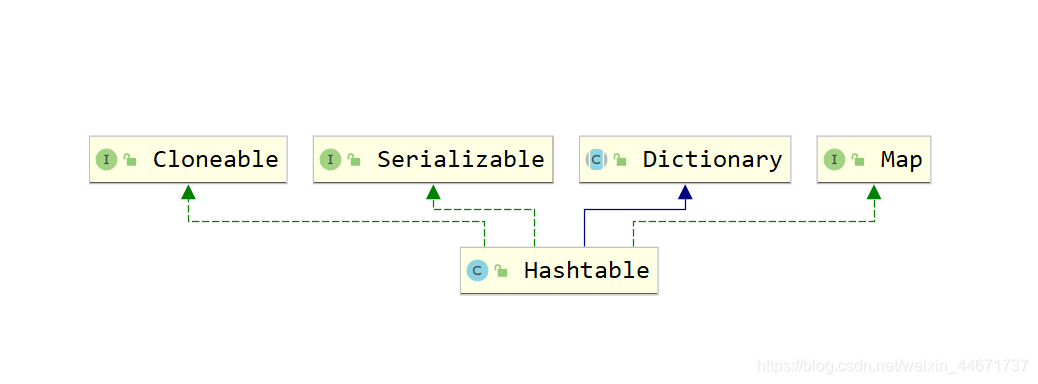
publicabstract
classDictionary<K,V>{
publicDictionary(){
}
publicabstractintsize();
publicabstractbooleanisEmpty();
publicabstractEnumeration<K>keys();
publicabstractEnumeration<V>elements();
publicabstractVget(Object key);
publicabstractVput(K key, V value);
publicabstractVremove(Object key);
}
//throws NullPointerExceptionifthe {@code key}is{@codenull}.
5.3.3 HashTable组成
/**
* The hash table data.
* 真正存放数据的数组
*/
privatetransient Entry<?,?>[] table;
/**
* The total number of entries in the hash table.
*/
privatetransient int count;
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. (The
* value of this field is (int)(capacity * loadFactor).)
* 重新hash的阈值
*@serial
*/
privateint threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hashtable.
*@serial
*/
privatefloat loadFactor;
5.3.4 HashTable中的Entry
finalinthash;
finalK key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
知道Entry是一个单链表即可,和HashMap中的Node结构相同,但是HashMap中还有Node的子类TreeNode。
5.3.5 put方法
publicsynchronized Vput(K key, Vvalue){
// Make sure the value is not null
if(value==null) {
thrownewNullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
inthash = key.hashCode();
//在数组中的位置 0x7fffffff 是31位二进制1
intindex = (hash &0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry !=null; entry = entry.next) {
//如果遍历链表找到了则替换旧值并返回
if((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value=value;
returnold;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key,value, index);
returnnull;
}
privatevoidaddEntry(inthash, K key, Vvalue,intindex){
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
//如果扩容需要重新计算hash,所以index和table都会被修改
if(count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash &0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
//插入新元素
tab[index] =newEntry<>(hash, key,value, e);
count++;
modCount++;
}
tab[index]= new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
5.3.6 get方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
publicsynchronized Vget(Object key){
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
inthash = key.hashCode();
intindex = (hash &0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for(Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e !=null; e = e.next) {
if((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return(V)e.value;
}
}
returnnull;
}
小编有话说:无论什么技术都要到项目实践才能真正掌握。优质项目下方免费领取!有springboot,springcloud,k8s等等,这次直接分享几乎涵盖了我们java程序员的大部分技术桟,可以说真的非常全面了。强烈建议大家都上手做一做,而且以后肯定用的上。资料包含高清视频+课件+源码……
领取资料:
点个在看你最好看




![[视频集合] 马云激情演讲80个 网上所有能搜到的都在这里了 全套](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/ba2c0d8f9f28f0e81213ce063dc38011.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[电子书集合] 50个 思科ccna所有电子书 汇总 批量下载 网上所有能知道到的都在这里](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/081d55fdf5c974edc3b38afa7597e14a.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[就业指导] Java面试专属视频 最新Java阿里京东美团滴滴面试题及答案教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/fb2f88633d9be374ae995992b13e7779.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)





![[就业指导] Java面试题专属视频 最新Java阿里京东美团滴滴java面试题及答案教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/be2bcf6c23bac0005fdd61e16024bd9c.png?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)




![[电子书集合] 120本PDF电子书打包下载 电脑攻防详解 新手集训营](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/097e7b590c5b016e8a8b2f80c6742f17.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)








![[Web开发合集] 首套SpringBoot课程 SpringBoot2.0不容错过的新特性 WebFlux响应式编程实](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/45f19ae070872350706095e0a7c3fb86.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[JAVA] 传智播客 java邮件开发实例视频15集 书籍作者主讲<邮件开发详解>](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/f78de148a5a09c7b6dcd70fb61d4b136.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
相关资源