python基础深浅拷贝
发布于 2021-04-17 05:44 ,所属分类:知识学习综合资讯
目录
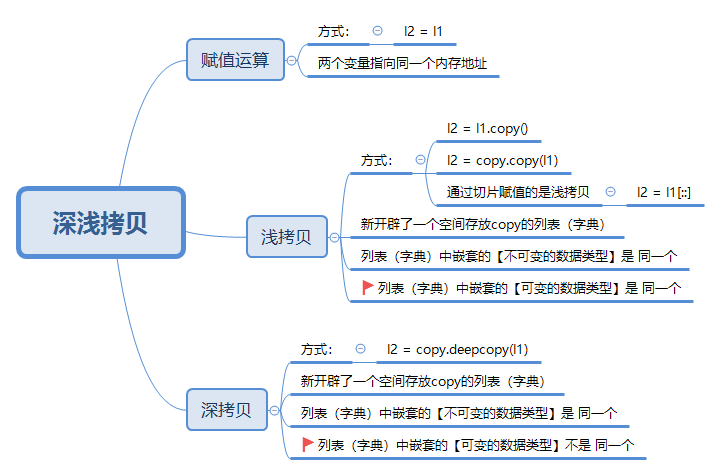
赋值运算
浅拷贝
深拷贝
详解
不可变的数据类型:缓存机制
可变的数据类型:深浅拷贝
(点击查看大图)
赋值运算
对于赋值运算来说,两个变量指向的是同一个内存地址,所以他们是完全一样的,任何一个变量对列表进行改变,剩下那个变量再使用列表的时候,这个列表就是发生改变之后的列表。
l1 = [1, 2, 3, ['pamela', 'apple']]l2 = l1print(l1 is l2) # Truel1[0] = 111print(l1) # [111, 2, 3, ['pamela', 'apple']]print(l2) # [111, 2, 3, ['pamela', 'apple']]l2[3][0] = 'abc'print(l1) # [111, 2, 3, ['abc', 'apple']]print(l2) # [111, 2, 3, ['abc', 'apple']]
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
浅拷贝
对于浅拷贝(copy)来说,只是在内存中新开辟了一个空间存放这个copy的列表(字典),但是新列表(字典)中的元素与原列表(字典)中的元素是公用的。(嵌套的可变的数据类型是同一个)
import copyl1 = [1, 'abc', True, (1, 2, 3), [22, 33], {'name': 'pamela', 'numbers': [123, 456, 789]}]l2 = l1.copy()# l2 = copy.copy(l1) # 与上一行代码一样,都是浅拷贝print(l1 is l2) # Falseprint(l1[0] is l2[0]) # Trueprint(l1[1] is l2[1]) # Trueprint(l1[2] is l2[2]) # Trueprint(l1[3] is l2[3]) # Trueprint(l1[-2] is l2[-2]) # Trueprint(l1[-1] is l2[-1]) # Trueprint(l1[-1]['name'] is l2[-1]['name']) # Trueprint(l1[-1]['numbers'] is l2[-1]['numbers']) # Trueprint(l1[-1]['numbers'][1] is l2[-1]['numbers'][1]) # True
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
l1 = [1, 2, 3, ['pamela', 123]]l2 = l1[::] # 浅拷贝print(l1 is l2) # False
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
深拷贝
对于深拷贝(deepcopy)来说,列表(字典)是在内存中重新创建的,列表(字典)中可变的数据类型是重新创建的,列表(字典)中不可变的数据类型是公用的。(嵌套的可变的数据类型不是同一个)
import copyl1 = [1, 'abc', True, (1, 2, 3), [22, 33], {'name': 'pamela', 'numbers': [123, 456, 789]}]l2 = copy.deepcopy(l1)print(l1 is l2) # Falseprint(l1[0] is l2[0]) # Trueprint(l1[1] is l2[1]) # Trueprint(l1[2] is l2[2]) # Trueprint(l1[3] is l2[3]) # Trueprint(l1[-2] is l2[-2]) # Falseprint(l1[-1] is l2[-1]) # Falseprint(l1[-1]['name'] is l2[-1]['name']) # Trueprint(l1[-1]['numbers'] is l2[-1]['numbers']) # Falseprint(l1[-1]['numbers'][1] is l2[-1]['numbers'][1]) # True
(左右滑动查看完整代码)



![[Python基础] 小甲鱼零基础入门Python学习视频+全套源码课件 Python视频教程 96讲](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/d7970e7abb546e6cbe9a4c45b030ed51.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)


![[Python基础] Python Web开发基础入门视频教程 目前最适合Python入门的视频教程 系统学习Python](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/c5d2bb19e1f9dd55f599179051f766e3.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[Python基础] Python零基础入门学习视频教程全42集](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/78b9d826631a1cf627f1eff51b54368b.png?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] 四周实现爬虫系统 超经典的Python零基础实战化教学 Python零基础实战课程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/570b1b552a766843b416fb28f2752248.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[Python基础] 小甲鱼零基础入门Python学习视频+全套源码课件 Python视频教程 96讲](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/f52ff23b8362685092ffda6c5fe1dbad.png?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[Python基础] Python Web开发基础入门视频教程 目前最适合Python入门的视频教程 系统](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/4f5c0cfab097fd030c7abdf05b57013f.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] 75节Python实战课程 Python基础篇+Python进阶篇+Python项目篇 Python三部曲 Pyth](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/fd5a6305469616cdc05c47fa0e881d00.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] 某机构Python基础班视频教程 13天课程 195个视频 非常接地气 Python编程基础教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/e842684397e882f374ce618ef1e850dd.png?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python基础] Python书籍+配套Python视频教程 Python编程实践视频教程+教材 27集](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/b364dba1a2c78a4c48253ac45aa2d605.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)


![[Python] 某机构Python基础班视频教程 13天课程 195个视频 非常接地气 Python编程基础教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/7ae6c7e3e4fe91fc43ad7a9f3c1f08a3.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)

![[Python] Python快速入门视频教程 快速掌握Python基础课程 猎豹网校Python视频教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/4c014989f94980d95f9022d89ce7cda5.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] Python基础+Pythonweb+Python扩展+Python选修四大专题 超强麦子学院Python35G视频](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/72f64a4f60ec6b3f27f8003601e81508.png?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)


![[Python基础] 老男孩Python全栈开发第二期培训视频教程 老男孩教育Python开发课程 基础课程篇](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/8e63050d4d3b2deaddefff89e0a5a66c.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] 智普教育Python培训就业班 150多集Python基础+就业视频教程](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/e8eee267ff320818f78b08bc7e0f586d.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
![[Python] 老男孩Python全栈开发视频教程 Python零基础系统学习Python开发视频+资料](https://static.kouhao8.com/sucaidashi/xkbb/e4942238b92e56e454abb60596981b02.jpg?x-oss-process=image/format,webp/resize,w_88/crop,w_88,h_88,g_nw)
相关资源