北美大厂8月第一周算法面试真题汇总
发布于 2021-08-05 13:11 ,所属分类:试题库考试资料大全
应广大同学们的需求,我们将定期整理各大厂最新的面试题题解,由我们【上岸算法】资深的老师给大家进行分析讲解,帮助大家实时掌握最新的面试动态,早日上岸!
题目描述:Remove Invalid Parentheses
s that contains parentheses and letters, remove the minimum number of invalid parentheses to make the input string valid.Example 1 :
Input: s = "()())()"
Output: ["(())()","()()()"]
Example 2:
Input: s = "(a)())()"
Output: ["(a())()","(a)()()"]
题 解
预处理判断出非法左右括号的个数,需要注意的是后出现的右括号是可以抵消一个先出现的左括号。然后根据左右括号非法的个数枚举每一个可以消除的点尝试消除。注意若消除一个左括号可以达到合法,但是存在多个连续的左括号的情况消除任意一个都是一样的结果,因此必须使用跳跃性dfs来实现跳过重复情况的操作。
参 考 代 码
class Solution {
public List<String> removeInvalidParentheses(String s) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int[] res = getLeftAndRightCount(s);
int leftCount = res[0];
int rightCount = res[1];
dfs(s, leftCount, rightCount, 0, result);
return result;
}
// 最小的移除次数肯定为leftCount + rightCount
public void dfs(String s, int leftCount, int rightCount, int index,
List<String> result) {
// dfs 出口
if (leftCount == 0 && rightCount == 0 && isValid(s)) {
result.add(s);
}
for (int i = index; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 连续相同的字符消除任意一个都是一样的情况,需要跳过
if (i > index && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i - 1)) {
continue;
}
// 若左括号多则尝试消除左括号
if (leftCount > 0 && s.charAt(i) == '(') {
String newStr = s.substring(0, i) + s.substring(i + 1);
dfs(newStr, leftCount - 1, rightCount, i, result);
}
// 若右括号多则尝试消除左括号
if (rightCount > 0 && s.charAt(i) == ')') {
String newStr = s.substring(0, i) + s.substring(i + 1);
dfs(newStr, leftCount, rightCount - 1, i, result);
}
}
}
// 若当前左右括号计数都为0则表示表达式合法
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int[] res = getLeftAndRightCount(s);
return res[0] == 0 && res[1] == 0 ;
}
// 遍历计算左右括号的总数,先左后右可以做消除
public int[] getLeftAndRightCount(String s) {
int leftCount = 0, rightCount = 0;
int[] counts = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
leftCount++;
}
// 碰到右括号的时候,判断是否可以消除左括号
else if(s.charAt(i) == ')') {
if (leftCount > 0) {
leftCount --;
}
else {
rightCount++;
}
}
}
counts[0] = leftCount;
counts[1] = rightCount;
return counts;
}
}
题目描述:Count of Range Sum
Given an integer array nums and two integers lower and upper, return the number of range sums that lie in[lower, upper]inclusive.
Range sum S(i, j) is defined as the sum of the elements in nums between indices i and j inclusive, where i <= j.
Example 1 :
Input: nums = [-2,5,-1], lower = -2, upper = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: The three ranges are: [0,0], [2,2], and [0,2] and their respective sums are: -2, -1, 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0], lower = 0, upper = 0
Output: 1
题 解
这题可以使用前缀和+归并排序的解法实现更加容易理解;
这边介绍树状数组解法,详情见注释,利用树状数组记录的是具体某一个值得个数,快速求得小于等于某值的所有个数总和。
参 考 代 码
class Solution {
static class BinaryIndexedTree {
private final int[] data;
private final int size;
public BinaryIndexedTree(int size) {
data = new int[size];
this.size = size;
}
/**
* BIT indexes: [0, 1, 2, ..., pos, pos + 1, ..., size - 1]
* ↑
* update position
*/
public void update(int pos, int delta) {
pos += 1;
for (int i = pos; i <= size; i += i & -i) {
data[i - 1] += delta;
}
}
/**
* BIT indexes: [0, 1, 2, ..., pos, pos + 1, ..., size - 1]
* ↑ ↑
* query range:[left right]
*/
public int query(int pos) {
pos += 1;
int result = 0;
for (int i = pos; i > 0; i -= i & -i) {
result += data[i - 1];
}
return result;
}
}
public int countRangeSum(int[] nums, int lower, int upper) {
// construct the sums array
long[] sums = new long[nums.length + 1];
sums[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sums[i + 1] = sums[i] + nums[i];
}
// prepare sorted sums for numberToIndex
long[] sortedNumbers = Arrays.copyOf(sums, sums.length);
Arrays.sort(sortedNumbers);
int result = 0;
BinaryIndexedTree BIT = new BinaryIndexedTree(sortedNumbers.length);
// 遍历的顺序是有sum[i]遍历,因此在以sum[i]为基础计算的时候,sum[i]之前的元素已经被更新到BIT中
// 基于排好序的sortedNumbers的下标建立树状数组
// 树状数组中 data[i] 表示数组 sum 中已经加入到BIT中的元素小于等于sum[i] 的个数有data[i]个
for (int i = 0; i < sums.length; ++i) {
// 区间值要在 [lower <= sum[i] - sum[?] <= upper]
// 因此 sum[?] <= sum[i] - lower sum[?] >= sum[i] - upper
// 所以小于等于 sum[i] - lower 的个数,减去 sum[i] - upper - 1 的个数,就是符合条件的个数
result += BIT.query(numberToIndex(sortedNumbers, sums[i] - lower)) - BIT.query(numberToIndex(sortedNumbers, sums[i] - upper - 1));
// 更新树状数组当中关联位置都 + 1
BIT.update(numberToIndex(sortedNumbers, sums[i]), 1);
}
return result;
}
/**
* find the last element no larger than `target`
*/
public int numberToIndex(long[] sortedNumbers, long target) {
int start = 0, end = sortedNumbers.length - 1;
while (start + 1 < end) {
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
if (sortedNumbers[mid] <= target) {
start = mid;
} else {
end = mid;
}
}
if (sortedNumbers[end] <= target) return end;
if (sortedNumbers[start] <= target) return start;
return -1;
}
}
题目描述
Given `n` orders, each order consist in pickup and delivery services.
Count all valid pickup/delivery possible sequences such that delivery(i) is always after of pickup(i).
Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Input: n = 1
Output: 1
Explanation: Unique order (P1, D1), Delivery 1 always is after of Pickup 1.
Input: n = 2
Output: 6
Explanation: All possible orders:
(P1,P2,D1,D2), (P1,P2,D2,D1), (P1,D1,P2,D2), (P2,P1,D1,D2), (P2,P1,D2,D1) and (P2,D2,P1,D1).
This is an invalid order (P1,D2,P2,D1) because Pickup 2 is after of Delivery 2.
题 解
每一个物品有取货送货两个操作,且送货必须在取货之后;针对于 n 个物品,最终一工会产生 2 * n 个操作。若此时再加入第 n + 1 个物品,相当于多了 2 步操作,我们需要计算的是这 2 步操作可以穿插在哪些操作中。很容易通过推导得出取货操作可以穿插在 2 * n + 1 个地方,对应每一种穿插位置,送货穿插的位置依次为 1, 2, 3, 4, ....., 2 * n + 1。
参 考 代 码
class Solution {
public int countOrders(int n) {
int mod = 1000000007;
long[] dp = new long[n + 1];
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (n == 2) {
return 6;
}
dp[1] = 1L;
dp[2] = 6L;
// 推导公式
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
int insertPoints = (i - 1) * 2 + 1;
// 当前新加入的物品可以穿插的取货送货的组合数
long count = (1 + insertPoints) * insertPoints / 2;
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * count) % mod;
}
return (int)dp[n];
}
}
题目描述:Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer distance. A pair of two different leaf nodes of a binary tree is said to be good if the length of the shortest path between them is less than or equal to distance.
Example 1 :
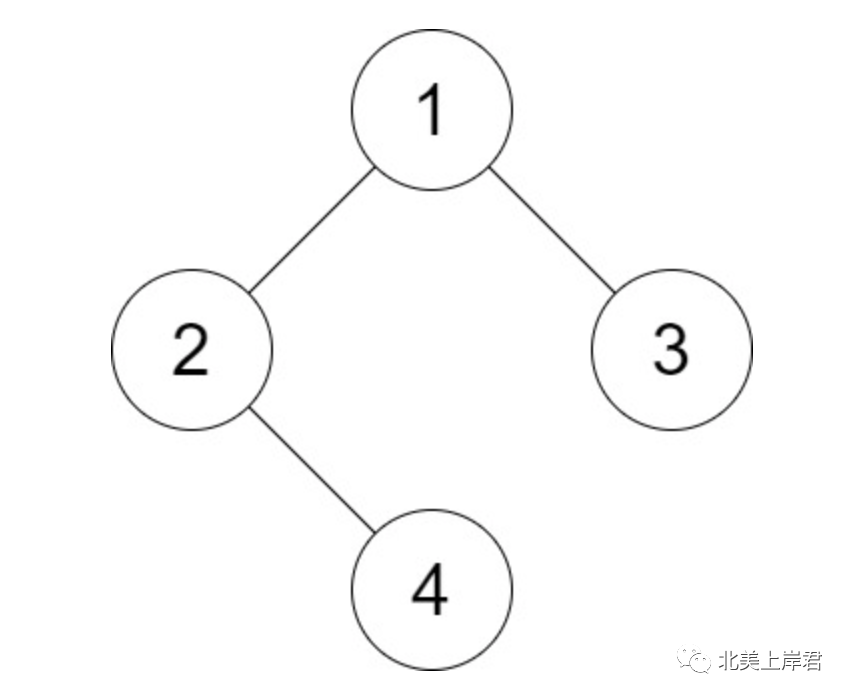
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], distance = 3
Output: 1
Explanation: The leaf nodes of the tree are 3 and 4 and the length of the shortest path between them is 3. This is the only good pair.
Example 2 :
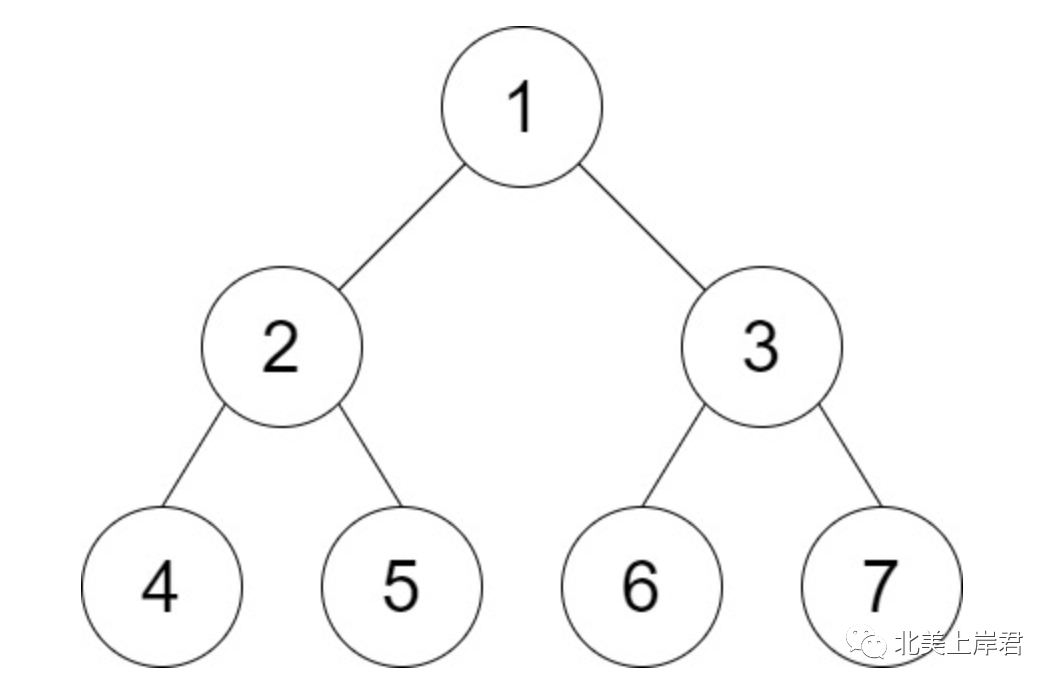
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], distance = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: The good pairs are [4,5] and [6,7] with shortest path = 2. The pair [4,6] is not good because the length of ther shortest path between them is 4.
题 解
分治法计算当前距离当前root节点的叶子节点满足条件的个数,若距离当前叶子节点距离为 L1 的左子树叶子节点个数有 n 个,右子树距离当前节点为 L2 的叶子节点个数有 m 个,若 L1 + L2 < d,则有效的叶子对为 n * m。使用 Map 来记录当前 root 节点左右子树的叶子节点距离及个数信息。
参 考 代 码
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int countPairs(TreeNode root, int distance) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
dfs(root, distance);
return res;
}
private Map<Integer, Integer> dfs(TreeNode node, int d) {
Map<Integer, Integer> disToCount = new HashMap<>();
if (node == null) {
return disToCount;
}
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
disToCount.put(1, 1);
}
// divide 分别计算左右子树的距离和节点个数信息
Map<Integer, Integer> leftInfo = dfs(node.left, d);
Map<Integer, Integer> rightInfo = dfs(node.right, d);
// conquer 在满足距离的情况下计算合法的叶子对数
for (int lDis : leftInfo.keySet()) {
for (int rDis : rightInfo.keySet()) {
if (rDis <= d - lDis) {
res += leftInfo.get(lDis) * rightInfo.get(rDis);
}
}
// 若距离当前root节点的距离为超过 d - 1, 说明还能再往当前root的父亲走过,因此距离 + 1
if (lDis + 1 < d) {
disToCount.put(lDis + 1, leftInfo.get(lDis));
}
}
// 右子树的判断也是一样
for (int rDis : rightInfo.keySet()) {
if (rDis + 1 < d) {
// 这边因为Map中记录的当前root的父亲,因此对于当前的disToCount,记录的整个当前root的子树
// 而有些距离在计算left的时候已经被更新过了
disToCount.put(rDis + 1, rightInfo.get(rDis) + disToCount.getOrDefault(rDis + 1, 0));
}
}
return disToCount;
}
}
杭州上岸算法网络科技有限公司

上岸算法网络科技有限公司是一家致力于用高质量,高互动性小班课程来帮助学生更好的在就业市场中定位以及求职的公司。我们以顶级的课程质量,高互动性的教学方式以及独特的小班教学模式来帮助学生更快的跨过求职的鸿沟,用最高效,经济,合理的方式帮助更多学生快速找到梦寐以求的工作。
Hadoop全新实战视频教程 Hadoop全新力作 徐培成老师Hadoop14天课程---第一周部分
Hadoop全新实战视频教程 Hadoop全新力作 徐培成老师Hadoop14天课程---第一周部分
【百度云】【事业单位资料包】事业面试真题汇总
【百度云】【事业单位资料包】事业面试真题汇总
玩转算法面试 从真题到思维全面提升算法思维
玩转算法面试 从真题到思维全面提升算法思维
Java进阶训练营
Java进阶训练营
【百度云】35套托福阅读考试真题汇总
【百度云】35套托福阅读考试真题汇总
【0粉开播】最新快手无人直播带货,一周出单
【0粉开播】最新快手无人直播带货,一周出单
小升初真题汇总
小升初真题汇总
一周进步:新媒体公众号运营课程
一周进步:新媒体公众号运营课程
机器学习与LeetCode算法面试班
机器学习与LeetCode算法面试班
Java大厂面试深度解析与实战
Java大厂面试深度解析与实战
老夏公务员面试通关课
老夏公务员面试通关课
AMC8初中基础能力历年真题及答案全套真题-百度一下载
AMC8初中基础能力历年真题及答案全套真题-百度一下载
【百度云】教师招聘面试 结构化面试通关班10讲结构化面试真题
【百度云】教师招聘面试 结构化面试通关班10讲结构化面试真题
周芳煜高一生物必修一
周芳煜高一生物必修一
高考生物 煜姐 周芳煜 二轮复习-真题详解
高考生物 煜姐 周芳煜 二轮复习-真题详解
【百度云】托福英语阅读十年真题134套汇总
【百度云】托福英语阅读十年真题134套汇总
一周学会Node.js开发电影微信公众号
一周学会Node.js开发电影微信公众号
传智播客张鹏带你一周hold住html+css
传智播客张鹏带你一周hold住html+css
全新Linux精品课程猿课CTO阿铭一周带你成Linux大神
全新Linux精品课程猿课CTO阿铭一周带你成Linux大神
全新Linux精品课程猿课CTO阿铭一周带你成Linux大神
全新Linux精品课程猿课CTO阿铭一周带你成Linux大神
尚硅谷Java面试题第一季 .
尚硅谷Java面试题第一季 .
某课266元-从真题到思维全面提升算法思维 - 难度中级
某课266元-从真题到思维全面提升算法思维 - 难度中级
高中生物 周芳煜 煜姐生物 2022年高考二三轮联报 真题全解
高中生物 周芳煜 煜姐生物 2022年高考二三轮联报 真题全解
算法面试通关40讲
算法面试通关40讲
烟草求职全攻略:网申笔试面试资料包
烟草求职全攻略:网申笔试面试资料包
初一数学方程几何如何突破?朱韬老师真题精讲带你攻克难点
初一数学方程几何如何突破?朱韬老师真题精讲带你攻克难点
算法面试通关40讲
算法面试通关40讲
【百度云】武峰2022第一期八周听写复述
【百度云】武峰2022第一期八周听写复述
2022高考真题原卷 解析卷 word文档
2022高考真题原卷 解析卷 word文档
周永亮高一数学2022寒假尖端班8讲完结
周永亮高一数学2022寒假尖端班8讲完结





























相关资源